Scallop Eyes as Inspiration for New Microscope Objectives
Neuroscientists at the University of Zurich have developed innovative objectives for light microscopy by using mirrors to produce images. Their design finds correspondence in mirror telescopes used in astronomy on the one hand and the eyes of scallops on the other. The new objectives enable high-resolution imaging of tissues and organs in a much wider variety of immersion media than with conventional microscope lenses.
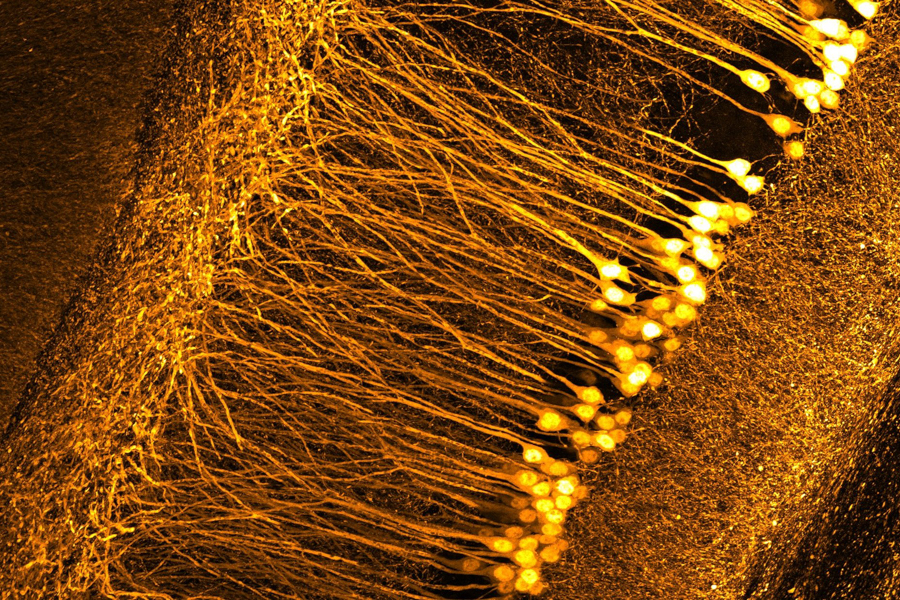
The Schmidt objektive produces detailed images of neurons in a mouse brain. Photo: Anna Maria Reuss (USZ) & Fabian Voigt (UZH)
Bernstein Members involved: Armin Bahl
Some species of mussels can see. Scallops, for example, have up to 200 eyes that help them detect predators such as an approaching starfish. However, the eyes of scallops differ significantly from the human eye. While in our eyes the combination of cornea and lens creates an image on the retina, in scallop eyes light is focused by a hemispherical mirror.
Optical imaging with lenses or mirrors
Creating images with mirrors instead of lenses is especially common in astronomical telescopes, in order to capture as much light as possible from planets, stars and galaxies. In the Schmidt telescope developed in the 1930s by Bernhard Schmidt (1879-1935) and still in use in many observatories today, a thin corrective lens is combined with a large spherical mirror.
Mirror objectives are rarely found, however, in microscopes used to study the biological microcosmos. Most microscope objectives are so compact that they can easily be assembled from lenses. However, to achieve the highest image quality, 10 to 15 lenses made of different types of glass are required, all of which must be precisely polished and accurately aligned with each other. As a result, the cost of microscope objectives for research can be equivalent to that of a medium-sized car, representing a significant portion of the total cost of a microscope.
Compatibility with different immersion media as stumbling block
In addition to their complex design, many commercial objectives have the disadvantage that they are usually designed for one specific immersion medium only, such as air, water or oil. This means that a new objective must be purchased for samples requiring a different immersion medium. For a long time, this was not a major problem, but in recent years, processes known as clearing techniques that can make tissue samples transparent have attracted a lot of interest in biology and pathology. For example, instead of laboriously preparing thin tissue slices from a removed mouse brain, clearing techniques can make the whole brain transparent. In pathology, the hope is that clearing techniques will increase the efficiency of biopsy-specimen examinations, making it possible to diagnose malignant tissue changes such as tumors earlier, for example. Unfortunately, however, most clearing techniques use immersion media that are incompatible with conventional microscope objectives. This means the considerable advantages of clearing techniques for research remain partially untapped.
High-resolution microscopy in large transparent tissue blocks
To circumvent the limitations of conventional microscope objectives, and inspired by the eyes of scallops, which in principle function like small underwater Schmidt telescopes, UZH neuroscientist and amateur astronomer Dr. Fabian Voigt developed an unconventional approach: he realized that it was possible to fill a Schmidt telescope with a liquid immersion medium and shrink it to the size of a microscope. The resulting objective is quasi a miniature telescope that has been submerged and still provides a sharp image. “It is possible to design a Schmidt objective in a way that it provides excellent image quality in any homogeneous fluid as well as in air,” says Voigt. This means that a single Schmidt objective is compatible with many different clearing techniques. The reason for this unusual feature is the use of a mirror instead of lenses. A spherical mirror focuses light at the same point whether it is immersed in liquid or is in the air.
Versatile applications also in medical diagnostics
To demonstrate the versatility of this innovative approach, researchers working with Fabian Voigt and UZH professor Fritjof Helmchen used their prototype Schmidt objective to study a variety of samples, including mouse brains, tadpoles and chicken embryos. Together with a team from Maastricht University, they were also able to analyze cleared human brain samples. In addition, the new type of objective is also suitable for measuring neuronal activity in the brains of live young zebrafish larvae. “In all cases, the image quality was equivalent to or even better than that achievable with conventional objectives – even though the Schmidt objective consists of only two optical elements,” Helmchen explains. Compared to conventional objectives, which have about a dozen more lenses, a Schmidt objective can therefore be manufactured much more cost-effectively.
Future applications could also include the examination of tumor tissues or the detection of neurological diseases. “In this respect, scallops could show us the way to improved medical diagnostics,” says Helmchen.




