Artificial Neurons – Research as Medial Artwork
Hermann Cuntz and Marvin Weigand from the Ernst Strüngmann Institute for Neuroscience (ESI) and the Frankfurt Institute of Advanced Studies (FIAS) had an exhibit at the Centre Pompidou. In this interview, they tell about how this chance arose and what their exhibit is about.
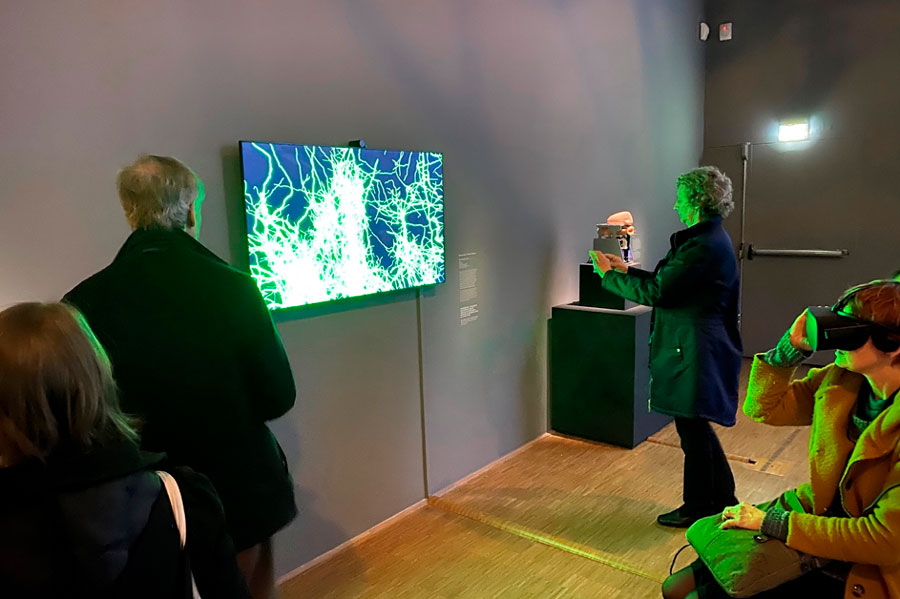

Visitors of the vernissage at the Centre Pompidou saw 'Computational Cajal' by Hermann Cuntz and Marvin Weigand. © Hermann Cuntz
/ESI/ Exhibiting at the ZKM or at the Centre Pompidou – for an artist that is like scoring a paper in Nature or Science for a researcher. However, for a researcher to show their work at one of the most renowned art museums of the world is quite unusual. The ESI scientists Hermann Cuntz and Marvin Weigand do it anyway. On February 26, the exhibition ‘Neurons – simulated intelligence’ opened at the Centre Pompidou in Paris. Among the artworks is an installation by the two brain researchers.
ESI: Hermann, exhibiting at a world famous art museum as an artist is exeptional as a researcher even more so. How did this come about?

Hermann Cuntz © ESI
Hermann Cuntz: It was a whole chain of events that led us to contribute to this exhibition at the Centre Pompidou. It actually started when my PostDoc boss Michael Häuser submitted one of the pictures of these artificial nerve cells for the Wellcome Image Awards competition. The theme was “most beautiful scientific picture of the year” or something along those lines. We actually won the prize and the picture was exhibited at the Wellcome Collection in London. This but also others of our pictures distributed pretty well around the internet and probably that’s why science journalists starting coming up to me. One thing led to another: Someone knew someone who knew someone and one day the ZKM (Centre for Art and Media Technology) in Karlsruhe contacted me and I made an exhibit for them. It was a 360-degree film in their PanoramaLabor, and they liked it so much that they asked me to do something for a biennial the ZKM organized in 2015. Marvin had just started his doctoral thesis with me and he came up with the idea of translating the whole thing into virtual reality. That made the whole thing extra cool and apparently also made an impression on people in the art scene. In any case, the curator of the exhibition at the Centre Pompidou knew our neurons through the ZKM Biennial. And indeed, one has to say that our visualization fits the theme of the exhibition very well.
The exhibition at the Centre Pompidou is called “Neurons – simulated intelligence” and is intended to be something like a journey through the history of artificial intelligence from an artistic perspective. But there are also quite biological exhibits – a brain in formaldehyde, for example. What does your piece look like?
Marvin Weigand: Basically, we show the cortical neurons that are produced by Hermann’s model. When visitors put on the VR glasses, they get to fly through 150 of those simulated neurons. You can control the direction of flight by moving your head. Occasionally a neuron fires an action potential – then it flashes. The whole thing is accompanied by rather spherical music, which helps to shut out the real world and completes the immersive experience that one wants to achieve with Virtual Reality.
Is it a strange feeling to contribute to an art exhibition as a scientist? And do you think your work actually has artistic value?
Hermann Cuntz: I think that if we have now made it to the ZKM and the Centre Pompidou, then what we do is art. That means, the science we do is a part of contemporary art. Of course, there are artists who have nothing to do with science, but we are obviously on a border or rather a transition between disciplines. Art and science blend into each other, you can’t really distinguish between them.
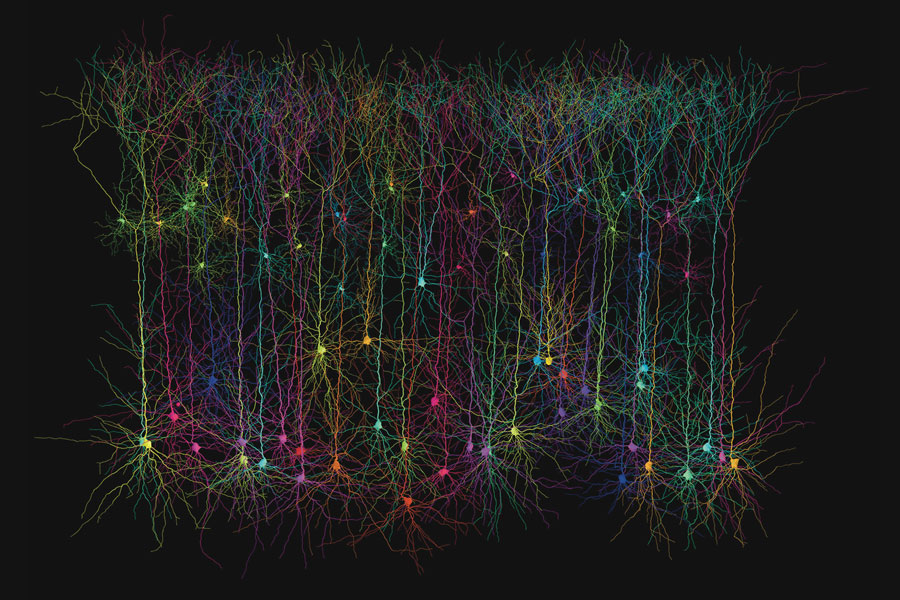
This computer-simulated image shows synthetic pyramid-shaped neurons of optimized size, shape and connectivity that are no different from those in the real biological brain. Pyramid cells have a pyramid-shaped cell body (soma) and are also characterized by long-branched dendrites. They are found in the front cortex (cortex and hippocampus) of mammals and are thought to be involved in cognitive functions.
ESI: Even though you are exhibiting and therefore somehow also an artist, you are actually scientists and make pictures and videos as part of your research – what scientific knowledge do you gain from your artificial neurons?
This computer-simulated image shows synthetic pyramid-shaped neurons of optimized size, shape and connectivity that are no different from those in the real biological brain. Pyramid cells have a pyramid-shaped cell body (soma) and are also characterized by long-branched dendrites. They are found in the front cortex (cortex and hippocampus) of mammals and are thought to be involved in cognitive functions. See https://www.esi-frankfurt.de/news/2020-02-27_cuntzweigandcentrepompidou/
Marvin Weigand: Strictly speaking, we do not really exhibit our research. The visualization, that is these artificial neurons that look like real biological preparations, are the byproduct of what we’re actually researching. We are interested in the general rules of the architecture of the nervous system. If we think we have discovered a possible rule, such as how neurons grow their dendrites, then we put this rule into a model that predicts what a dendrite that grows according to these rules would look like. And the more realistic the artificial dendrite looks later, the better we understood the general rule behind it.
Hermann Cuntz: The pyramidal cells that we are exhibiting at the Centre Pompidou for example, come from an article I published a few years ago. In that study, I looked at dendrites not only of pyramidal cells, but from all kinds of neurons and from many different species. The paper is called “One Rule to Grow Them All” and we show that a basic rule for the growth of dendrites is to keep the cable length as short as possible and the signal transmission as fast as possible. So if you know where the cells are a dendrite has to get its inputs from, then you can calculate with our model how the optimal dendrite should look like. And the same rules can be applied over different species, over different cell types. This works in all the cases we have tried. And one of the nice things about this model is that it passes the Turing test right from the beginning. You can give these cells – the visualization of the cell – to an expert and he can no longer differentiate: Is this a real neuron or is it artificial. In fact, it once happened that a colleague gave a lecture at our institite and said in the introduction: Of course, it will never be possible to reproduce this beautiful variety of real nerve cells in a computer model. And then he showed my picture of artificially created neurons. Obviously this is a fantastic confirmation for us that we did something right. Of course, it’s not enough to count as reliable evidence, but it is an indication.
ESI: So, the visualization of the neurons is a test whether you have made correct assumptions. But the VR element is just a joke that you thought up for the artwork without any practical, scientific use for it?
Hermann Cuntz: I wouldn’t say so. Marvin’s implementation in VR allows for people who work with similar models or approaches as we do, to have the possibility to visualize the artificial cells immersively in three dimensions. And not just individual neurons, but within a network of cells. The more cells you want to look at in context, the more difficult it is to keep track. And if you can so to say experience the constellations in VR spatially, it definitely helps to gain a better understanding. Marvin may have been the first to translate neurons into VR five years ago, but there are now other groups that are doing it simply because they are coming up against the same limits of visual perception as we are.
Marvin Weigand: In fact, I would like to publish the VR implementation, not necessarily as a paper, but as a program for virtual reality glasses. Free to download for everyone. I think it could have a pretty high impact because it is still very new. And regardless of whether it is now relevant for scientific work, we could certainly reach people who have nothing to do with research and increase interest in neuroscience in general. Just now, while I was setting up the exhibition in the Centre Pompidou, a security guard approached me and said that generally speaking, he wasn’t really interested in modern art, but that he thought our piece to be very nice and he wanted to know more about it.
What’s next on your agenda, art or research?
Hermann Cuntz: Both. We’re currently talking with an Israeli artist couple about a new, interactive project. But of course most of our time and energy goes into research. One of our next projects is to study cell types not in isolation, but in a cell compound. We are now in a position to no longer let the cells grow alone in empty space, but also packed together in a piece of cortex for example. So, we are now trying to make all the cell types that we now of grow together in one simulation. And in the end, of course, we hope that we will be able to simulate electron microscopic images taken from real tissue. This will enable us to say: We expect our model to look like this – does it? If not, we still have to change something. If so, then we have already understood a lot about neural architecture.




